Kubernetes application logging with fluentd
Application logging in a kubernetes cluster is very easy. In this tutorial we will generate a logging concept for applications deployed on a kubernetes cluster. To save the logs and query them we use elasticsearch, for displaying them we use Kibana and for collecting the logs we use fluentd.
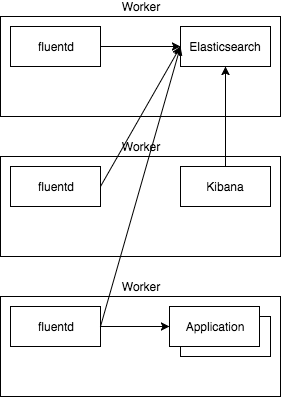
fluentd will be deployed as DaeomSet, so it runs on each node in the cluster and collects logs from the directories /var/log and /var/lib/docker/containers. Therefor hostPath volumes are used that are mounted into the fluentd container. Then fluentd will send the logs to elasticsearch where they are stored in the index logstash-* for queries. Kibana is used to display the logs and visualize them.
It is very easy to deploy it, first we need an elasticsearch server deployment and service (please pay attention this is not production grade logging):
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: logging
---
apiVersion: apps/v1beta2
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: es
namespace: logging
labels:
app: elasticsearch
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: elasticsearch
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: elasticsearch
spec:
containers:
- name: elasticsearch
image: docker.elastic.co/elasticsearch/elasticsearch:5.6.3
env:
- name: "discovery.type"
value: "single-node"
- name: "ES_JAVA_OPTS"
value: "-Xms256m -Xmx256m"
- name: "xpack.security.enabled"
value: "false"
resources:
requests:
memory: 300Mi
ports:
- containerPort: 9200
name: http
protocol: TCP
- containerPort: 9300
name: transport
protocol: TCP
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: elasticsearch
namespace: logging
labels:
app: elasticsearch
spec:
type: LoadBalancer
selector:
app: elasticsearch
ports:
- name: http
port: 9200
protocol: TCP
- name: transport
port: 9300
protocol: TCP
After the elasticsearch cluster is running in the logging namespace we deploy the fluentd service as DaeomSet and connect it to the elasticsearch Database:
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: DaemonSet
metadata:
name: fluentd
namespace: logging
labels:
k8s-app: fluentd-logging
version: v1
kubernetes.io/cluster-service: "true"
spec:
template:
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: fluentd-logging
version: v1
kubernetes.io/cluster-service: "true"
spec:
tolerations:
- key: node-role.kubernetes.io/master
effect: NoSchedule
containers:
- name: fluentd
image: fluent/fluentd-kubernetes-daemonset:elasticsearch
env:
- name: FLUENT_ELASTICSEARCH_HOST
value: "elasticsearch"
- name: FLUENT_ELASTICSEARCH_PORT
value: "9200"
- name: FLUENT_ELASTICSEARCH_SCHEME
value: "http"
resources:
limits:
memory: 200Mi
requests:
cpu: 100m
memory: 200Mi
volumeMounts:
- name: varlog
mountPath: /var/log
- name: varlibdockercontainers
mountPath: /var/lib/docker/containers
readOnly: true
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 30
volumes:
- name: varlog
hostPath:
path: /var/log
- name: varlibdockercontainers
hostPath:
path: /var/lib/docker/containers
After this fluentd will watch for new logs and send them to the elasticsearch service.
As last component we need the kibana dashboard to visualize the logs:
apiVersion: apps/v1beta2
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: kibana-logging
namespace: logging
labels:
app: kibana-logging
kubernetes.io/cluster-service: "true"
addonmanager.kubernetes.io/mode: Reconcile
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: kibana-logging
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: kibana-logging
spec:
containers:
- name: kibana-logging
image: docker.elastic.co/kibana/kibana:5.6.2
resources:
limits:
cpu: 1000m
requests:
cpu: 100m
env:
- name: ELASTICSEARCH_URL
value: http://elasticsearch:9200
- name: XPACK_MONITORING_ENABLED
value: "false"
- name: XPACK_SECURITY_ENABLED
value: "false"
ports:
- containerPort: 5601
name: ui
protocol: TCP
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: kibana
namespace: logging
labels:
app: kibana-logging
spec:
type: LoadBalancer
selector:
app: kibana-logging
ports:
- name: http
port: 5601
protocol: TCP
---
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: ingress
namespace: logging
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: "nginx"
spec:
rules:
- host: logging.url.de
http:
paths:
- path: /
backend:
serviceName: kibana
servicePort: 5601
Now there should be a complete logging environment available that can be accessed, in my case via the ingress url.
After this we only need to add the logstash-* index to Kibana, now we should visualize the logs:
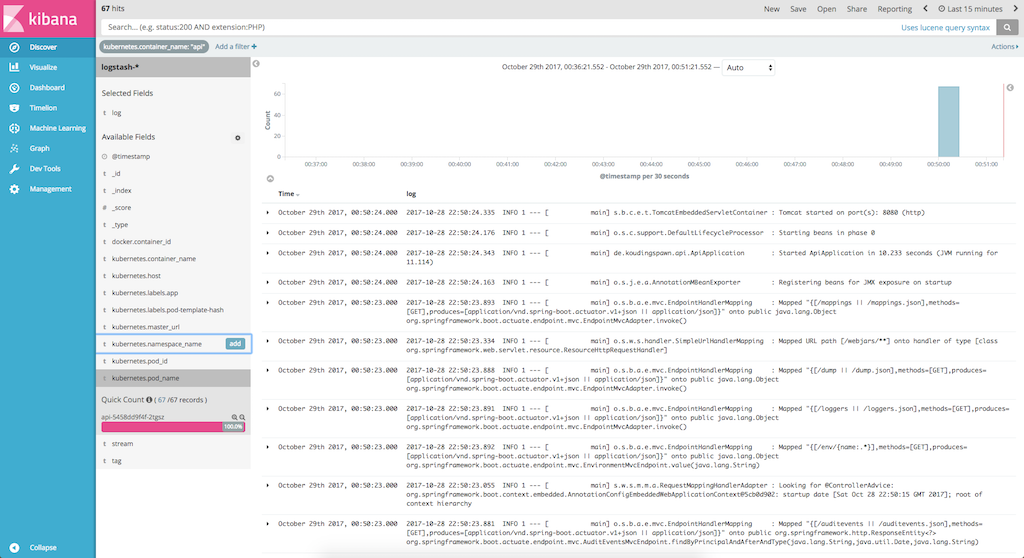
One very interesting part is the available fields list, this allows us to query for specific containers or for example for requests made via nginx-ingress.
One problem of this solution is, that the elasticsearch containers are not persisted, if the container fails all data are lost. One solution might be to add persistentVolume to a container like glusterFS. At the same time, it is important to note that if the cluster fails, the logs may not be accessible.

